Search Results for: cell locomotion
Cell locomotion
Cell locomotion (Science: cell biology) movement of a cell from one place to... Read More
Locomotion
Definition noun The ability of cells or organisms to move and propel itself from place to place Supplement Locomotion in... Read More
Cytoskeleton
Definition noun plural: cytoskeletons cy·to·skel·e·ton (cell biology) The lattice or internal framework of a cell... Read More
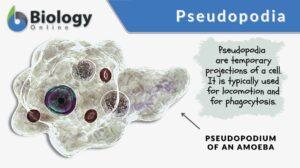
Pseudopodia
A pseudopodium (plural: pseudopodia) refers to the temporary projection of the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell. Pseudopodia... Read More
Microfilament
Definition noun plural: microfilaments mi·cro·fil·a·ments, mī'krō-fil'ă-mĕnts A thin, helical, single-stranded... Read More
Cell matrix
Definition noun plural: cell matrices cell ma·trix, ˈmeɪtɹɪks An insoluble, dynamic gel in the cytoplasm, believed... Read More
Centrosome
Centrosome Definition What is a centrosome? The centrosome is considered to be the main microtubule-organizing... Read More
Microtubule
Microtubule Definition noun plural: microtubules mi·cro·tu·bule, mī'krō-tū'byūlA cytoplasmic tubule made up of... Read More
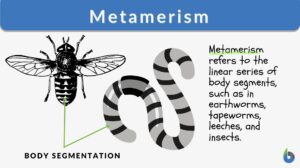
Metamerism
Metamerism Definition Metamerism is the repetition of homologous body segments. This type of development can be seen in the... Read More
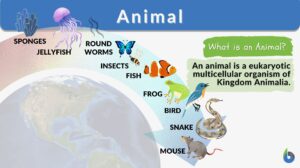
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Intermediate filament
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Intermediate filaments
Definition noun plural: intermediate filaments A type of cytoskeleton characterized by having a diameter ranging from 8... Read More
Actions of Caffeine in the Brain with Special Reference to Factors That Contribute to Its Widespread Use
IV. Actions of Caffeine on Brain Functions and BehaviorHaving discussed the molecular and neuronal actions of caffeine,... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
Smooth muscle
The smooth muscle can be described as a type of muscle in the human body that is non-striated and involuntary in action.... Read More
Cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration Definition What is cellular respiration in simple terms? Cellular respiration can be defined simply as... Read More
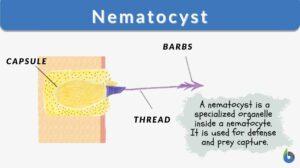
Nematocyst
All organisms are composed of millions of cells. Many cells serve specific purposes and are specialized to do distinct... Read More
Flagellate
Definition noun, plural: flagellates A cell or an organism that has flagella adjective (1) Of, pertaining to, characterized... Read More
Chlorophyta
Chlorophyta Definition Chlorophyta is a taxonomic group (a phylum) comprised of green algae that live in marine habitats.... Read More
Density dependent inhibition of growth
Density dependent inhibition of growth (Science: cell culture) The phenomenon exhibited by most normal (anchorage dependent)... Read More
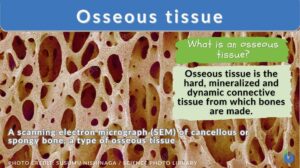
Osseous tissue
What Is Bone Or Osseous Tissue? Osseous tissue is the structure providing, hard and mineralized connective tissues. Osseous... Read More
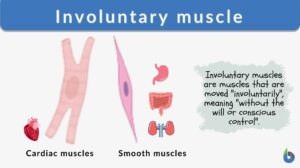
Involuntary muscle
A muscle act typically either under the control of the will or without conscious control. Muscles that can be controlled at... Read More
Streaming movement
streaming movement The form of movement characteristic of the protoplasm of leukocytes, amoebae, and other unicellular... Read More
Muscle tissue
Definition noun, plural: muscle tissues An animal tissue capable of contracting, and therefore enables movement or tension... Read More
Skeletal muscle
Definition noun, plural: skeletal muscles A voluntary, striated (vertebrate) muscle that is associated with the skeleton,... Read More
Hyaloplasm
Definition noun (1) The liquid component of the cytoplasm. (2) The liquid portion of the nucleoplasm, as in nuclear... Read More